Abstract
Background: Transplacental transfer and breastfeeding are the main transport routes of organic pollutants into children at the beginning of life. Although pollutant transmission through these mechanisms primarily depends on the maternal pollution burden, its impact may be modulated by physiological effects.
Objectives: We have examined whether gestational weight gain (GWG) exerts an influence on the content of lipophilic low volatile pollutants in breast milk.
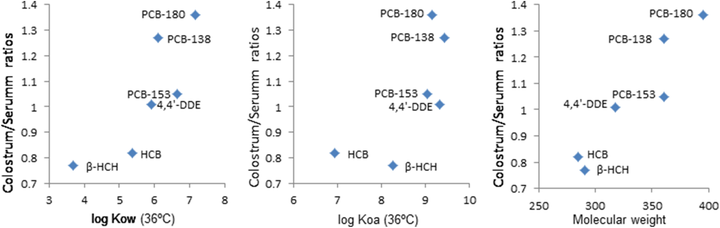
Results: Colostrum from mothers from the INMA cohorts of Sabadell and Gipuzkoa (n = 256 and 119, respectively) with low GWG as defined by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) from the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine had significantly higher concentrations of polychlorobiphenyls (PCBs) and 4,4’-DDE than colostrum in mothers who gained weight within IOM recommendations or in those who exceeded this threshold. Statistically significant differences were also found in the colostrum:maternal serum ratios of these compounds. Women with low GWG retained higher pollutant amounts in colostrum. These observations are consistent with previously described higher concentrations of these pollutants in infant cord blood from mothers with low GWG by IOM standards. They indicate that mobilization of lipophilic organic pollutants by metabolic pregnant changes not only leads to higher fetal transfer but to higher accumulation into the mammary system upon low GWG.
Conclusions: The present results show that insufficient GWG, besides increasing in utero exposure, also enhances pollutant transfer to infants during breastfeeding which considerably extends the significance of this physiological change for the pollutant children intake in early life.
Keywords: Breastfeeding; Gestational weight gain; Maternal transfer of organic pollutants; Organohalogen compounds.